La función de un TVS (Supresor de Tensión Transitoria) es proteger los circuitos electrónicos de daños causados por sobretensiones transitorias (como rayos y descargas electrostáticas). Garantiza la seguridad del circuito al bloquear y desviar rápidamente la energía de las sobretensiones. En el diseño de circuitos de protección TVS, se suele conectar una resistencia en serie, como se muestra en la Figura 1, donde una resistencia de 22 Ω se conecta en serie con las líneas de recepción y transmisión del circuito de interfaz de comunicación RS232. El TVS se conecta en serie con la resistencia para absorber energía durante eventos de sobretensión, protegiendo el circuito y limitando la corriente. Esta configuración garantiza que, cuando el circuito se ve amenazado por una sobretensión transitoria, el TVS pueda intervenir rápidamente y absorberla eficazmente, protegiendo así a otros componentes del circuito. Al mismo tiempo, la resistencia en serie regula aún más la magnitud de la corriente, evitando que el TVS se dañe por una corriente excesiva mientras absorbe la sobretensión.
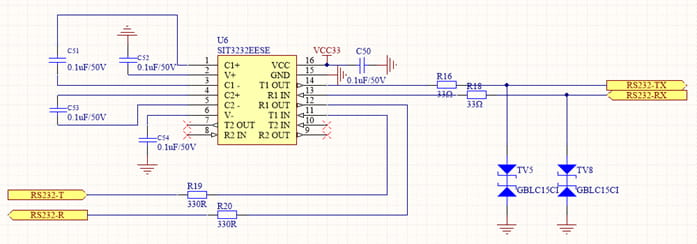
Figura 1 Interfaz de comunicación RS232
Generalmente, existen dos maneras de conectar un TVS con una resistencia en serie: una es colocar la resistencia después del TVS, como se muestra en la Figura 2, y la otra es conectar la resistencia antes del TVS, como se muestra en la Figura 3. Estos dos métodos varían según la aplicación. El método de conexión frontal puede reducir la corriente de entrada, mientras que el método de conexión trasera permite una división de tensión secundaria y una limitación de corriente más eficaces.
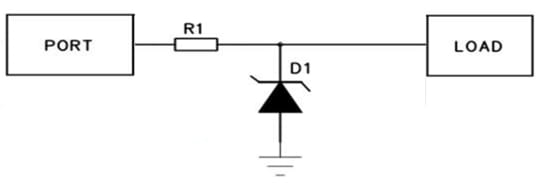
Figura 2

Figura 3
En el circuito mostrado en la Figura 2, el dispositivo TVS absorbe inicialmente la mayor parte de la corriente de entrada. Posteriormente, cualquier tensión o corriente residual restante se divide y se limita de nuevo mediante la resistencia R2. Este diseño protege la carga aguas abajo con mayor eficacia. Sin embargo, si la impedancia de la carga aguas abajo es mucho mayor que la de la resistencia R2, el efecto de división de tensión y limitación de corriente se reduce considerablemente, y la función de la resistencia R2 se ve reducida.
En el circuito mostrado en la Figura 3, considerando la magnitud de la corriente de entrada, si la sobretensión es pequeña, se puede seleccionar una resistencia de potencia adecuada y colocarla antes del TVS. De esta manera, la resistencia compartirá una pequeña porción de la corriente, reduciendo así la corriente de entrada (IPP). En consecuencia, la tensión de sujeción Vc del TVS también disminuirá en consecuencia, mejorando aún más el efecto de protección en la carga aguas abajo.

Xml política de privacidad blog Mapa del sitio
Derechos de autor
@ Micro-Magic Inc Reservados todos los derechos.
 RED SOPORTADA
RED SOPORTADA
